This podcast was first published by The Crude Life on June 28, 2024.
David LaGreca, Managing Director of Voluntary Carbon Markets Services, EcoEngineers, joins Jason Spiess and Steve Bakken on Townsquare Media’s SuperTalk 1270 Talk of the Town to share his experience working on the first voluntary carbon sequestration for ethanol in the nation.
Voluntary carbon sequestration involves the capture and storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) through various projects funded by private entities. This process aims to offset emissions by removing CO2 from the atmosphere or preventing its release. These projects often include reforestation, afforestation, and soil carbon enhancement, among others.
Key Aspects of Voluntary Carbon Sequestration:
-
Market Dynamics: Voluntary carbon markets allow businesses and individuals to purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions. These credits finance projects that sequester carbon, contributing to overall climate goals.
-
Verification and Standards: Projects in voluntary carbon markets must adhere to stringent verification and monitoring standards to ensure their effectiveness. Organizations like Verra and the ICVCM set these standards, ensuring that carbon credits represent real and verifiable climate benefits.
-
Global Initiatives: Various global initiatives and evolving models are enhancing the structure and credibility of voluntary carbon markets, making them more robust and effective in addressing climate change.
-
Economic Incentives: Voluntary carbon credits direct private financing to climate-action projects, enabling initiatives that might not receive funding otherwise. This can stimulate economic growth while promoting environmental sustainability
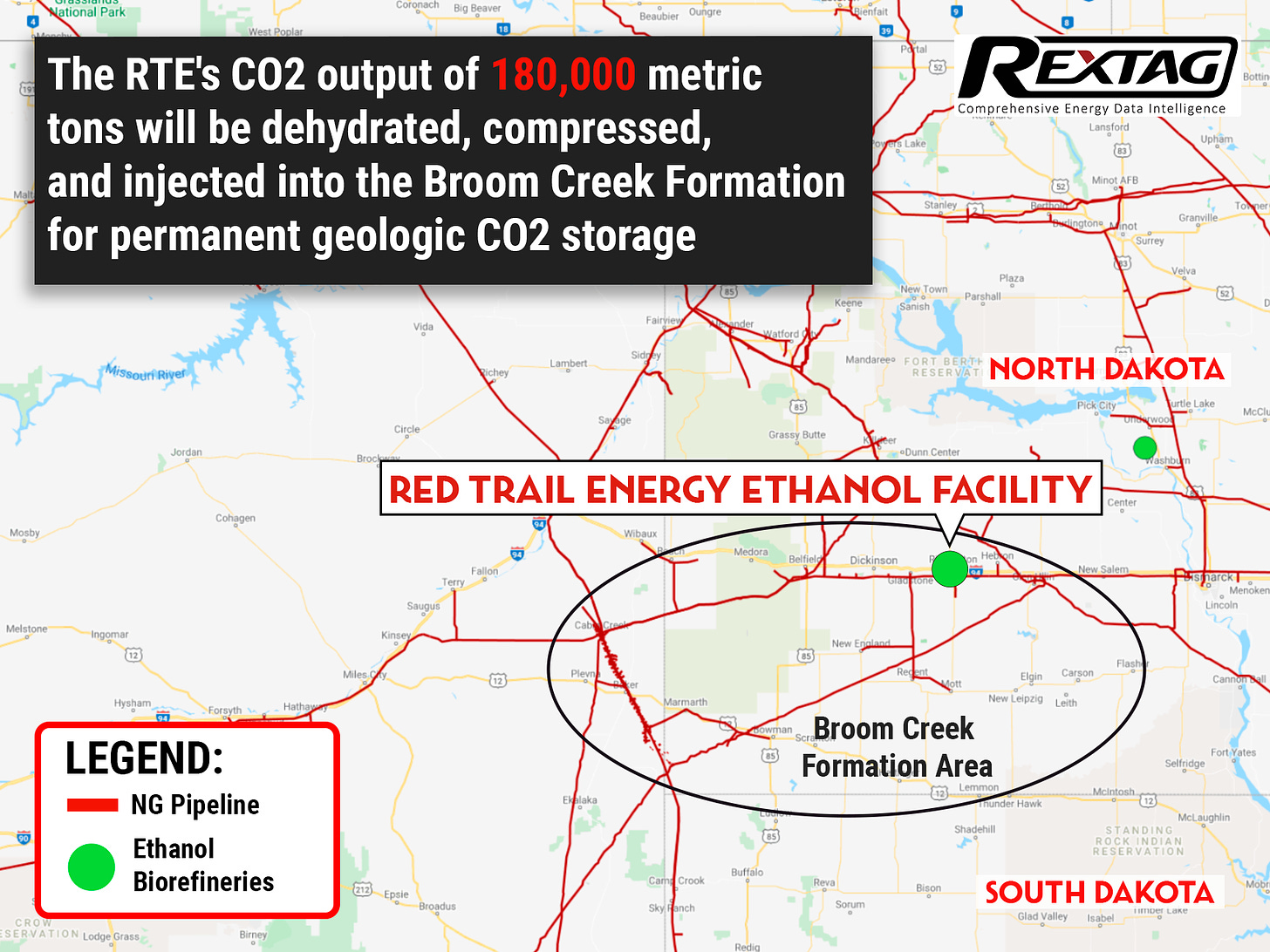
The Red Trail Energy (RTE) Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) project represents a significant milestone in the integration of carbon capture technology within the ethanol production industry.
Located near Richardton, North Dakota, this project is a pioneering effort to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from ethanol production, making it more sustainable and competitive in markets with stringent low-carbon fuel standards.
Project Overview
The RTE CCS project officially commenced operations in July 2022. This project involves capturing CO2 emissions from the ethanol production process and securely storing them underground. This initiative aims to capture more than 90% of the CO2 emissions produced by the ethanol facility, significantly reducing its carbon footprint.
Technology Used
The CCS technology employed by RTE includes several advanced components:
-
Capture: CO2 is captured from the fermentation process during ethanol production. This step involves separating CO2 from other gases using amine-based solvents.
-
Compression: The captured CO2 is compressed to a supercritical state to facilitate transport and injection.
-
Transportation: The supercritical CO2 is transported via pipelines to the injection site.
-
Injection and Storage: The CO2 is injected into deep geological formations, such as saline aquifers, where it is securely stored and prevented from entering the atmosphere.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Implementing CCS at RTE’s ethanol plant brings both environmental and economic benefits. By significantly reducing CO2 emissions, the project helps mitigate climate change impacts.
Additionally, it enhances the competitiveness of RTE’s ethanol in markets with low-carbon fuel programs, potentially leading to economic incentives and regulatory advantages.
Milestones and Statistics
-
Start of Operations: The project began capturing and storing CO2 in July 2022.
-
Capture Efficiency: The technology can capture over 90% of the CO2 emissions from the ethanol production process.
-
Emissions Reduction: The project aims to reduce the net CO2 emissions of the ethanol plant, contributing significantly to the overall goal of lowering the carbon intensity of ethanol fuel.
Conclusion
The Red Trail Energy CCS project is a landmark development in the ethanol industry, showcasing how advanced carbon capture technology can be effectively integrated to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
This project not only positions RTE as a leader in sustainable ethanol production but also sets a precedent for other industrial facilities aiming to lower their carbon footprints.
To contact LaGreca, click here for his LinkedIn Profile or Company Website.